Money machine
How much is a college degree really worth?
In 2009, Donald Hart found himself in an enviable position.
Leading up to his graduation from Ocean Lakes High School in Virginia Beach, Hart had been accepted to a slew of the state’s public, four-year universities: Virginia Tech, the University of Virginia, Old Dominion University, George Mason University and James Madison University.
Attracted by the convenience of studying close to home, as well as the opportunity to play trumpet in the university’s new marching band, he wound up choosing ODU. But there was another reason ODU stood out from the competition: sticker price.
For the 2009-2010 academic year, ODU’s annual tuition and fees came to $7,318, a price tag that would increase to $8,450 by the time Hart graduated in 2013 with a bachelor’s degree in criminal justice and about $15,000 in school debt. ODU charged less than most other Virginia public universities Hart considered, and the tuition and fees didn’t even factor in room and board, or the cost of moving to a different city. He wanted to get the best value for his money.

“That was a little bit of a factor, too,” Hart recalls. “I’m like, ‘Well, do I want to have extra debt, or do I just want to get a degree and [start a career]?”
After graduation, Hart landed a job with New York Life Insurance Co., which provided matching contributions that helped him pay off his student loan debt about two years ago. After a stint working in New York City, he’s back in Virginia Beach, training financial advisers for the insurance company, earning about $140,000 to $160,000 annually, including bonuses.
“If I look back, finishing college, I would never have guessed I [would be] where I am today at all,” Hart says. “The critical thinking skills and the building relationships and doing different things while in college, I think that all … [helped] mold me to be successful in really any business I would have chosen.”
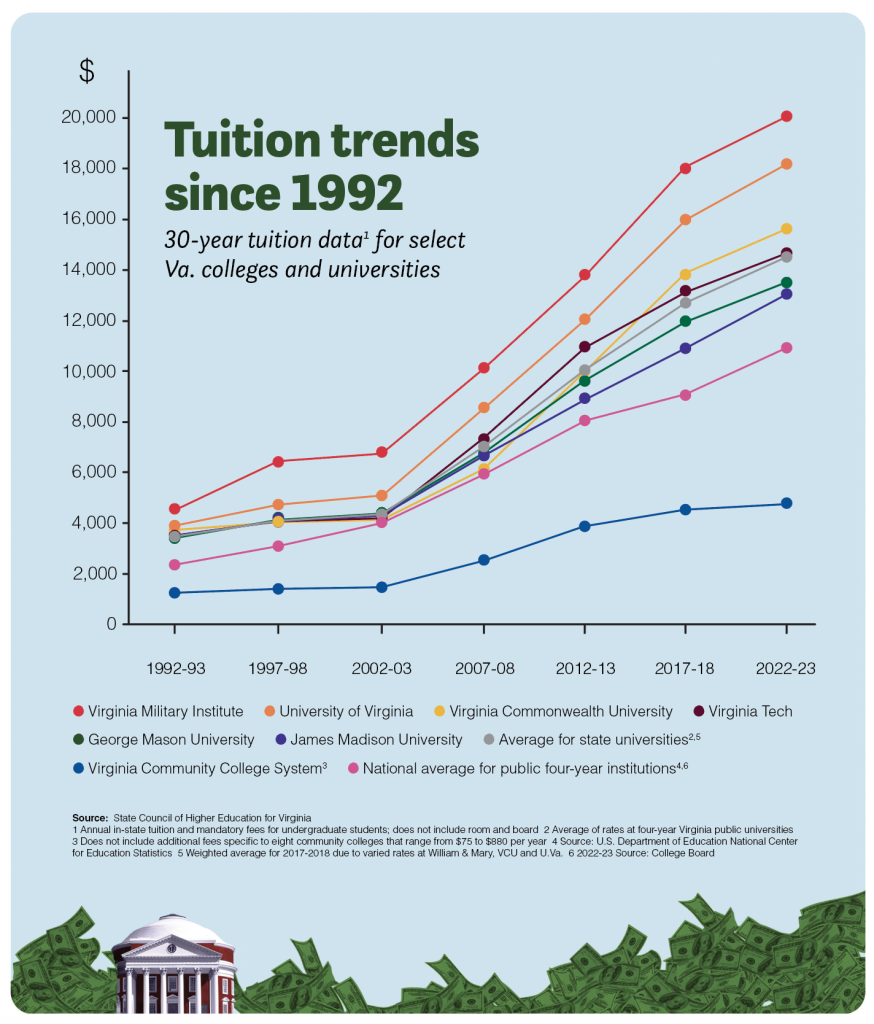
Since Hart graduated a decade ago, the cost of going to college in Virginia has continued to escalate, now averaging $14,538 per year across the state’s 15 public four-year colleges and universities, according to data from the State Council on Higher Education for Virginia. That’s up from $10,387 in the 2013-2014 academic year — a nearly 40% increase over the past decade.
With the cost of earning a degree soaring to new heights — the national average to attend a four-year public university in 2022-2023 was $10,950 annually for tuition and fees, according to the College Board — fewer people are heading off to college, and debate has ensued over the value of postsecondary education. (Enrollment numbers could be further chilled, academics say, by the U.S. Supreme Court’s June ruling overturning a Biden administration plan to wipe out more than $400 billion
in student debt.)
Furthermore, amid a tight labor market, policymakers and employers are placing less emphasis on four-year degrees and more on certificate programs and other nondegree career pathways.
Perhaps the most prominent example can be found in a new state government hiring policy. Effective July 1, in an effort to attract more state workers, Gov. Glenn Youngkin eliminated degree requirements and/or preferences for about 90% of state job listings. (Maryland implemented a similar change in 2022.)
Nevertheless, even amid record tuition rates, a college or university degree remains the likely best avenue for increasing one’s lifetime earning power, experts say, providing a return on investment unrivaled by stocks or bonds.
“Investing in a college education for many people will be the second biggest investment they ever make, probably after buying a house,” says Martin Van Der Werf, director of editorial and education policy at Georgetown University’s Center on Education and the Workforce (CEW). “It’s more expensive than buying a car, which is probably the other major purchase many people face in their lives. So, to actually understand what you’re going to get from that investment … is a pretty important piece of data.”
What it’s worth
Graduating from a public four-year university can add from $765,000 to more than $1 million to an individual’s lifetime earnings in the U.S., according to a 2021 report prepared for SCHEV by Virginia Commonwealth University‘s L. Douglas Wilder School of Government and Public Affairs focusing on postcollege outcomes among public college and university graduates from 2007 to 2018.

Forty years after enrolling — or about the length of a career — average graduates of four-year public colleges can expect a net economic gain of $1.03 million in adjusted earnings, compared with $984,000 for the average private nonprofit college graduate, according to the Georgetown report, which ranked 4,500 U.S. colleges, including community colleges, public two- and four-year institutions, private nonprofit colleges and for-profit colleges, by their return on investment.
Ten years after enrollment, though, the story is a bit different. Community colleges and institutions that offer associate degrees and certificate programs provide better short-term returns because graduates can get to work quickly, often with less debt and fewer years of study than their four-year counterparts, CEW found. Over the decades, however, four-year graduates have much greater earnings power. (A 2019 CEW study found that associate degree and certificate holders brought in a median $141,000 in 10-year adjusted net earnings, compared with $107,000 for all college graduates.)
“College typically pays off, but the return on investment varies by credential, program of study and institution,” CEW Director Anthony P. Carnevale says in a statement. “It’s important to inform people about the risk of taking out loans but not graduating, which could leave them without the increased earnings that would help them repay those loans.”
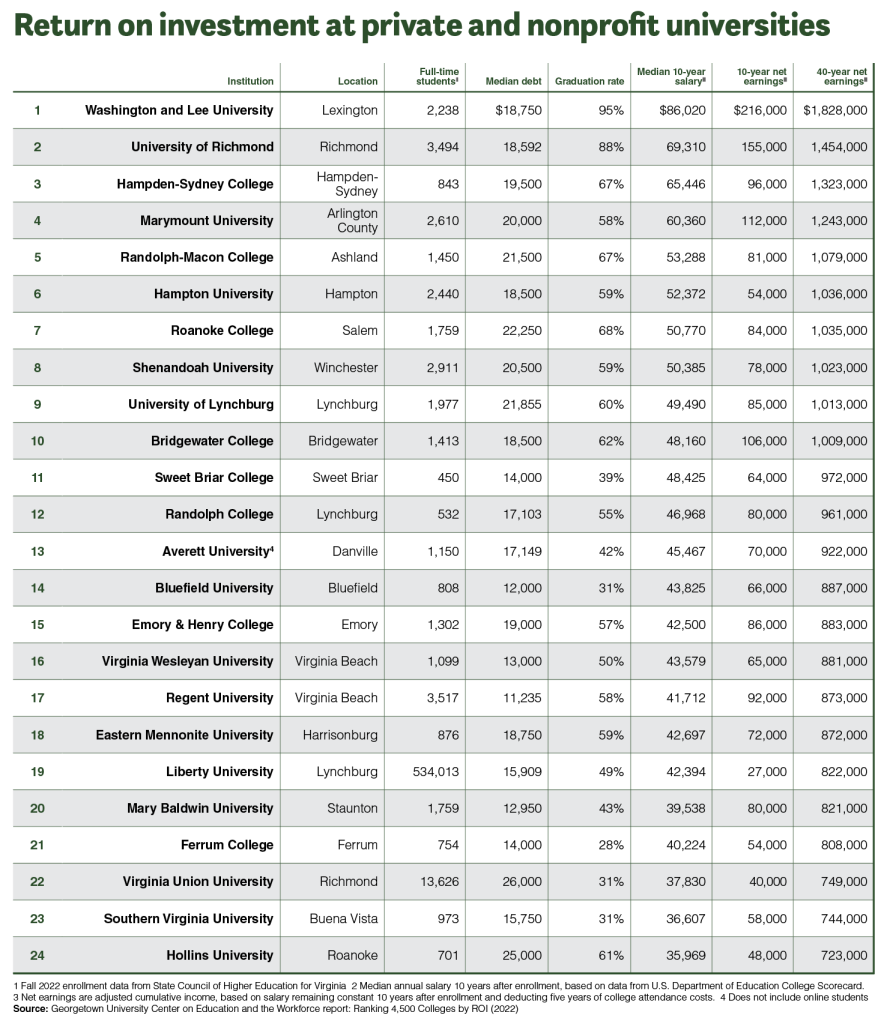
Here in Virginia, it may come as no surprise that some of the state’s most prestigious public and private universities rank higher than their in-state peers when it comes to return on investment. Examining how much money a degree could bring a graduate over a 40-year career, private liberal arts school Washington and Lee University leads the way at $1.82 million, followed by U.Va. with $1.64 million and Virginia Tech at $1.55 million, according to Georgetown’s 2022 report.
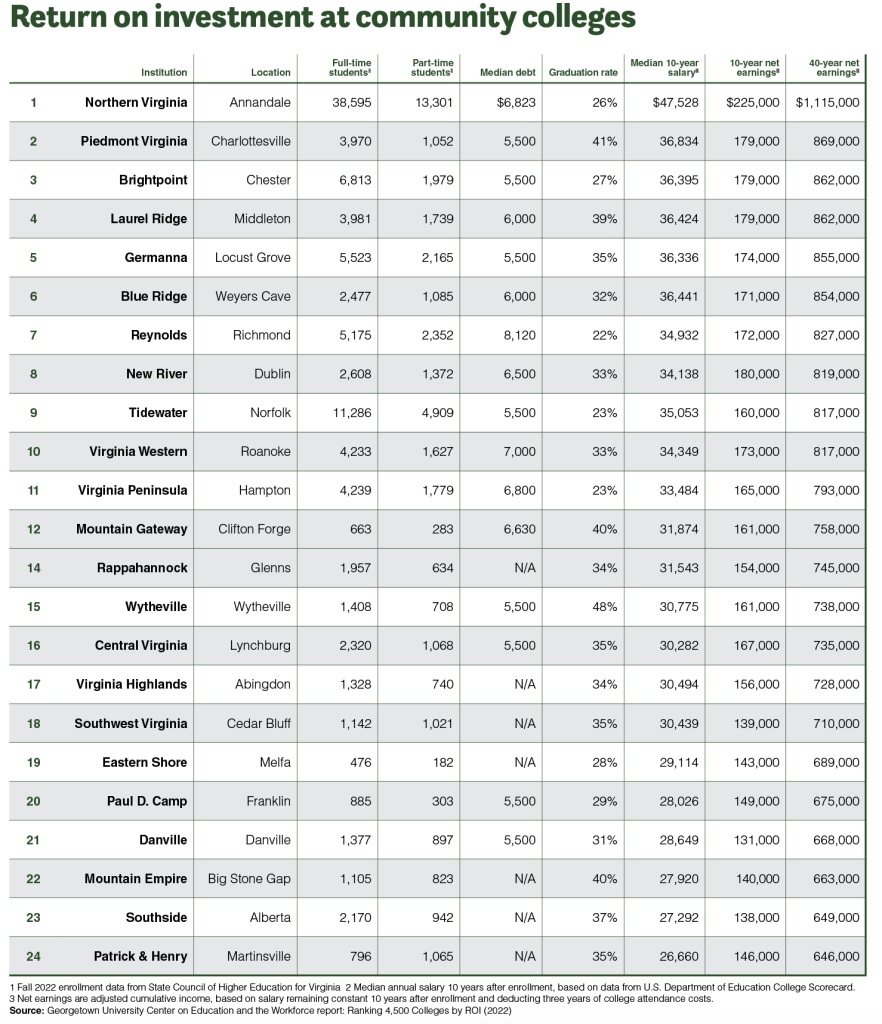
After just 10 years, however, Newport News-based Riverside College of Health Careers, a private, not-for-profit school offering associate degrees and certificates in health care, ranks No. 1 for return on investment, bringing $263,000 in adjusted net earnings, followed by Northern Virginia Community College at $225,000, according to CEW’s data. Washington and Lee ranks No. 3 for 10-year net earnings, at $216,000.
It takes less time and less money to earn an associate degree or certificate, Van Der Werf, one of the study’s authors, says. While some students enroll in community college with plans to transfer to a four-year institution, others are seeking a quick career boost, such as a promotion or other job opportunities, after earning an associate degree or credential.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median weekly earnings of bachelor’s degree graduates in 2022 was $1,432, compared with $1,005 for associate degree holders and $853 for workers with just a high school diploma.
“Basically … having a college degree leads to greater earnings,” Van Der Werf says.

‘Shopper’s mentality’
Earnings are only one data point that experts consider when examining a college degree’s potential ROI; the broader picture can be much more nuanced, based on a variety of factors. For instance, pay may vary depending on where someone lives. And universities with higher graduation rates generally produce graduates with higher earnings. Majors matter, too — a professional with a bachelor’s degree in engineering may make a higher salary than a worker with an arts and humanities degree.
According to the VCU report, 56.3% of 15,348 survey respondents who earned a certificate, associate or bachelor’s degree from a Virginia higher education institution said their education was worth the cost. That’s a satisfaction rate that varies when broken down by degree type, race, gender, discipline, geography and graduation year; for example, 64% of those who majored in STEM disciplines agreed their education was worth the cost, compared with 47.6% of liberal arts graduates.
During the past five years at Virginia Tech, parents and prospective students have been asking more and more frequently about return on investment — including more affluent families, says Juan Espinoza, director of admissions and associate vice president for enrollment and degree management. “If you’re looking at affordability,” he says, “you’re also looking at ROI. You can’t disconnect the two.”
Families have more of a “shoppers’ mentality” these days, given the national conversation about whether college is worth it, says Espinoza, a 2004 Tech graduate who was a first-generation college student. In particular, parents want to know about student success, including graduation rates, which were 85% at Virginia Tech last year, according to SCHEV. “I think it’s a legitimate question,” he says, “and one that colleges need to be able to explain to students and their families.”
University officials frequently point to student success when talking about ROI, and that’s a value that may transcend a padded bank account. A college education, they contend, can lead to healthier life outcomes, greater civic participation and upward social mobility.
Getting ahead
At George Mason University, many students “are starting behind the start line,” says Saskia Campbell, GMU’s executive director of university career services, citing the university’s history of educating a diverse student body, including those from disadvantaged backgrounds.
Forty years after enrollment, a GMU bachelor’s degree recipient is likely to see a net economic gain of $1.4 million, ranking GMU No. 6 among Virginia’s public and private nonprofit colleges and universities for that data point, according to Georgetown’s study. And while GMU had a 91.4% admittance rate for the 2021-2022 school year, it also had a 70% graduation rate.

“To me, that is the very definition of social mobility,” says David Burge, vice president for enrollment management. “You give people a chance to be successful, you support them while they’re on their journey and as they exit and are always there for them as they come back, and you will build that reputation by delivering something of value.”
Among the signs of a GMU degree’s value, Campbell points out, is that 89% of GMU graduates are working in a role related to their career goals within six months. GMU’s location in Fairfax County and proximity to major companies is another example. More than 600 employers, including Fortune 500 companies like Reston-based General Dynamics Corp. and McLean-based Capital One Financial Corp., recruit on campus, and there’s a waitlist of others wanting to participate in career fairs. “And that’s just my office,” she says.
Maggie Tolan, VCU’s senior assistant vice president for student services, wrapped up new student orientation in June. Her presentation to incoming freshmen — a third of whom are first-generation college students — included a diagram of a bobsled.
“If I just give you the textbook on how to bobsled, you’re not going to be a good Olympic bobsledder, right?” Tolan asks. “You’re going to need to practice. A lot of what we talk about at VCU is there’s your degree, but it’s really what you’re doing in the four years to build the résumé, to build the network.”
VCU’s tools for student success include “major maps,” year-by-year charts that help students set goals in categories ranging from degree planning to developing career skills and preparing for life after college. VCU also requires students to participate in real-world experiences like internships.
It has a high acceptance rate (92% for the 2021-2022 academic year), but a lower graduation rate (67%) than some of its similarly sized peers. However, bachelor’s degree holders from VCU — where the colleges of Art and Humanities and Sciences are the largest — can expect their degrees to net them $1.03 million in earnings power over a 40-year career, according to Georgetown’s study.
“For our [graduates] … we are earning … 77% more than a high school graduate that never went to college,” says Tolan. “I think that’s a pretty good darn investment.”
Buyer beware
Those who tout higher education’s return on investment also acknowledge that student loan debt remains a huge concern.
About 1 million Virginians owed $41 billion in federal student loan debt in 2020, according to the VCU Wilder report. While a college degree holder may make more money over the course of a career than people who didn’t earn a degree, Tod Massa, SCHEV’s director of policy analytics and data warehousing, offers a “buyer beware” caveat.
“College is not for everyone. And, unless you can afford it, I don’t think you should see the college experience as an experience to purchase,” Massa says. While college is a “high value opportunity,” it’s not a guarantee a student will land a particular job, he says. Prospective students and families should also consider what they value about education.
Nationally, undergraduate enrollment remains about 6% to 7% below pre-pandemic levels. About 1.16 million fewer undergrad students were enrolled in spring 2023 than in spring 2020, according to a May report from the National Student Clearinghouse Research Center. Undergraduate admissions at Virginia’s 15 four-year public universities performed better, declining just 2% between fall 2020 and fall 2022, according to an analysis of SCHEV data.
Enrollment in the state’s 23 public community colleges has also declined, from a 2011 peak of 197,226 to 146,553 in fall 2022 (up slightly from 144,215 in fall 2021). There tends to be a direct relationship between low unemployment and community college enrollment dips, Massa explains.
Virginia Community College System Chancellor David Doré, (see related Q&A) calls student debt one of the “most significant problems in the country right now,” adding that the system needs to do a better job of marketing itself to become more nimble, faster and better designed around students’ needs.
With more than 51,000 full- and part-time students, Northern Virginia Community College, is by far the state’s largest two-year public college. NOVA has a labor market team that studies regional job posting data as well as long-term government forecasts to keep up with the region’s needs, says Steve Partridge, NOVA’s vice president of strategy, research and workforce innovation. The team frequently consults area employers about their needs in order to better structure learning and programs. Still, Partridge says, the school can’t keep up with the regional demand for IT workers.
Many of NOVA’s students work while attending school — 38,595 are part-time students, according to 2021-2022 SCHEV data. Students who are already in the working world are likely to be more focused on the income they’d like to make, adding to their determination to reach their goals.
“I think the working adult has a much better view of that ROI, because they’re often self-funding,” Partridge says. “When they borrow, they know what they’re borrowing, because they’re probably also paying the rent. … They’re very, very interested in what the job market is going to look like when they graduate and where the opportunities will be when they graduate.”
-