Clean slate
Power utilities, state government look to carbon-free future
M.J. McAteer //August 30, 2021//
Clean slate
Power utilities, state government look to carbon-free future
M.J. McAteer //August 30, 2021//
On April 17, 2020, with a flourish of the pen, Virginia Gov. Ralph Northam reshaped the future of energy production in the commonwealth.
Signing the Virginia Clean Economy Act (VCEA) into law last year, Northam declared that Virginia would become a leader in fighting climate change, and, indeed, no other Southern state has passed legislation as comprehensive. Sen. Jennifer McClellan, D-Richmond, the act’s co-patron, seconded the governor’s optimism. She adds that the VCEA will not only provide Virginia with clean energy but boost its economy, already projected to grow 8% in 2021, due in part to green energy jobs.
The VCEA requires stringent energy-efficiency standards that are projected to generate as much as $3,500 in savings for the average Virginia household over the next 30 years, according to a study by Advanced Energy Economy, an industry trade association. The act’s headline-grabber, though, is its mandate that all electricity consumed in the commonwealth must have zero carbon emissions and be generated from renewable energy sources by 2050.
It’s an ambitious goal, and the onus for achieving it falls largely on its two biggest electricity suppliers, Richmond-based Dominion Energy Inc., with about 2.5 million in-state customers, and Ohio-based Appalachian Power, which services about 524,000 customers in Southwest Virginia, the Roanoke and New River valleys and the Lynchburg area. The two utilities are working purposefully to comply with the act, which gives Dominion until 2045 and Appalachian until 2050 to comply, with a provision allowing extensions if the utilities can’t provide reliable service from carbon-free sources by that point.
“You can either view this legislation as presenting a significant challenge or a great opportunity. We see it as the latter,” says Ed Baine, president of Dominion Energy Virginia. “We are making great progress toward Virginia’s clean energy future and delivering significant benefits to our customers.”
Where things stand
The efforts to move Virginia to carbon-free energy production are happening as the impacts of climate change are becoming more apparent across the globe. The Pacific Northwest and Northern Europe saw record heat waves this summer, while several European nations experienced catastrophic flooding.
In August, the United Nations issued a report stating humans “unequivocally” caused climate change, warning that global warming is nearing a tipping point. Atmospheric carbon dioxide is at its greatest concentration in at least 2 million years, temperatures are at a 6,500-year high and sea levels are rising at the fastest rate in 3,000 years, according to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change report.
U.N. Secretary-General António Guterres called it a “code red for humanity,” adding, “The alarm bells are deafening. This report must sound a death knell for coal and fossil fuels, before they destroy our planet.”
Last year, under the Northam administration, Virginia passed the VCEA and became the first Southern state to join the Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative, a coalition of mid-Atlantic and Northeastern states working to combat climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions from the power sector.
Close to 60% of the energy generated by Dominion in the commonwealth has been coming from sources that are neither carbon zero nor renewable, primarily natural gas and some coal. The Fortune 500 utility plans to close its coal-burning Chesterfield Power Station by May 2023, and it’s projected to close the coal-burning Clover Power Station in Halifax County in 2026. Dominion wants to keep its Virginia City Hybrid Energy Center — which burns coal, waste coal and biomass — operational until 2045.
Will Cleveland, a senior lawyer with the Southern Environmental Law Center, opposes that plan. He calls the center “a net loser” that should be shuttered much sooner. The energy center may be profitable to Dominion, he says, but the power company’s customers pay for it through site-specific surcharges on their electric bills known as rate adjustment clauses.
Most of the rest of Dominion’s energy supply in Virginia — about 40% — is generated from its four nuclear plants in North Anna and Surry. Nuclear energy is carbon zero, so it can remain in play under the VCEA. The Surry facilities are federally licensed to be operational until the early 2050s, and Dominion is seeking an extension to run the North Anna facilities until 2060. Despite having an option to build a third nuclear plant at North Anna, the utility has no current plans to do so, says Dominion’s manager of media relations, Rayhan Daudani.
Appalachian’s reliance on fossil fuels is heavier than Dominion’s. About 45% of its generating capacity comes from coal and another 28% from natural gas, with nuclear energy making up just 7% of its portfolio. (The remaining 20% comes from a mix of sources, including wind, hydroelectricity and pumped storage hydropower.)
Appalachian has no coal-burning plants in Virginia, but it does operate two in West Virginia: the 2,930-megawatt John Amos plant and the 1,330-megawatt Mountaineer plant. About half the power from these plants flows to Virginia customers. Under the VCEA, that eventually will have to stop unless Appalachian employs renewable energy certificates to offset that consumption. Against the objections of environmental groups such as the Sierra Club, Appalachian is seeking to keep these coal-burning plants operating until 2040.
The Sierra Club says that keeping the plants open is not cost-effective for customers, but Appalachian President and Chief Operating Officer Chris Beam has a different take. “If forced to make big changes up front, that would drive [consumer] prices up,” he says.
Nevertheless, to conform to federal regulations regarding wastewater systems and ash removal, the plants require $250 million in upgrades, and Appalachian is asking the State Corporation Commission to approve a $2.50 monthly rate increase to pay for the improvements. If approved, the rate increase would take effect in October.
Both companies as well as the commonwealth have their work cut out to comply with the VCEA and all will, by necessity, be making historic investments in wind power, solar power and energy storage.
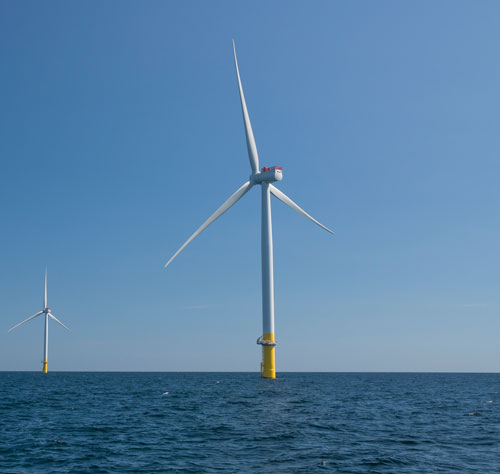

Where the wind blows
Making wind power into a dominant source of energy for Virginia won’t be a breeze. Already, opposition has put the brakes on building the state’s first proposed land-based wind farm.
The planned 14-turbine Rocky Forge Wind project in the mountains of Botetourt County is opposed by the Virginians for Responsible Energy, a citizens’ group that contends that the project would degrade the landscape and pose a fire hazard. A lawyer for the group recently pointed out to the county that Rocky Forge developer Apex Clean Energy had missed a deadline for a site approval plan. After some back and forth, the county then rejected Apex’s request for an extension, leaving the project becalmed.
The Sierra Club, however, “fiercely supports” Rocky Forge. Dan Crawford, chair of the club’s Roanoke group and of its Virginia onshore wind promotion, says, “If push comes to shove, and it goes to court, I’m confident the wind farm will happen.”
Rocky Forge is also part of the state government’s plan to meet its goal of obtaining at least 30% of the electricity required for state agencies from renewable sources by 2022.
Meanwhile, Dominion is entering the offshore wind business in a mammoth way with its Coastal Virginia Offshore Wind project, a $7.8 billion, 2.6-gigawatt wind farm to be built about 27 miles offshore from Virginia Beach. Baine says it is the largest project in Dominion’s history. It also will be the country’s largest and first utility-owned wind farm, featuring about 180 wind turbines, each rising more than 800 feet above the ocean surface. Once in operation, it’s estimated that the wind farm will generate $11 million annually in state and local tax revenues, according to a study by Glen Allen-based Mangum Economics commissioned by the Hampton Roads Alliance.
At this point, the project, sited in a federal lease area, is undergoing federal regulatory review and does not appear to have hit significant headwinds. The Virginia Department of Mines, Minerals and Energy (DMME) has been working with the U.S. Bureau of Ocean Energy Management and the Army Corps of Engineers to keep the project moving as part of the Biden administration’s goal to make all electricity generation in the country green by 2035. DMME director John Warren says that a timeline to establish a second federal lease area in Virginia waters for other offshore wind projects is already in development.
Construction on the Coastal Virginia Offshore Wind farm is expected to begin in 2024. To facilitate that, Dominion is building the nation’s first U.S.-chartered wind-turbine-installation ship, the Charybdis, in Brownsville, Texas. The $500 million vessel will be able to install a wind turbine a day, with a 2026 target completion date.
Appalachian’s plans to tap into wind power are much more modest. Beam says that Appalachian will add about 200 megawatts of onshore wind power in the next five years, with an eventual goal of reaching 2,200 megawatts.

Solar systems
Just six years ago, Dominion was generating only 1 megawatt of electricity from solar power — or enough to provide electricity to 250 households. Daudani blames that puny figure on solar not being cost-competitive. Since then, though, costs have come way down, and Dominion now has 5,249 megawatts of solar in operation or under development, including nine projects that the Virginia State Corporation Commission approved in May. At optimum output, these nine facilities will be capable of powering 125,000 homes.
Appalachian plans to add 210 megawatts of solar in the next five years, but Beam cautions that “the size of the projects can and may change.” His company’s end goal is to have 3,400 megawatts of solar by 2050.
Just like the wind farm in the Blue Ridge, however, land-use issues surrounding solar have begun to crop up. The VCEA specifies that all solar farms generating power for the commonwealth must be located in Virginia, and it is estimated that Virginia will need about 60 square miles of solar panels to meet its energy needs in 2050. Most of these solar farms will be in rural areas.
In June, in what could be a harbinger of battles to come, Frederick County supervisors rejected a proposal to build an 80-acre solar plant near Gore, citing concerns about preserving agriculture land and the area’s rural character. Hollow Road Solar LLC subsequently filed a $7.5 million lawsuit against the supervisors.
“Are there challenges related to land use?” says Dominion’s Baine. “Yes. There is a wide range of views on land use and property rights, [but] we are working with each and every locality to support their needs.”
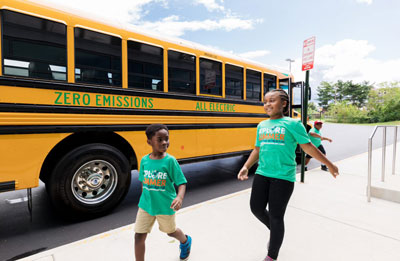
The Southern Environmental Law Center is a supporter of solar energy, but Cleveland cautions that “the purpose is not to overbuild, but to keep the lights on.” He would like to see more effort going into locating solar facilities on marginal sites such as brownfields, landfills and abandoned parking lots instead of on agricultural land. But he agrees with DMME’s Warren about initiatives to locate solar farms on previously mined sites in far Southwest Virginia. Warren calls that “a win-win situation for everyone.”
In addition to the state eyeing old mining sites for solar farms, Warren says the state government also has purchased power agreements on six solar farms as part of its 2022 goal and is encouraging community colleges to implement solar systems to generate power for individual buildings.
Warren sounds a warning, though, about the eventual success of the VCEA. The infrastructure for all green power initiatives will require mineral extraction, he says, something that many environmentalists oppose. “Establishing a domestic raw material supply chain is not environmental treason,” he says. “We have to flip the script, or we are headed down a big collision course.”
Energy storage
Of the three main sources of green energy, storing energy produced by sources like solar and wind presents the biggest challenge. The VCEA stipulates that Dominion and Appalachian must have 2,700 megawatts and 400 megawatts of storage capacity respectively by 2035, but so far, costs remain high and storage technology is less than satisfactory.
“Batteries are still pretty expensive compared to alternatives,” says Beam with Appalachian. He expects prices will come down in the next five to 10 years, but, for now, his company has a couple of bidders on small storage projects.
Dominion is investing $33 million in four pilot storage projects for a combined 16 megawatts of energy storage capacity but, once tapped, that power will last just four hours. “We’d like to see that duration get longer,” says Baine. For now, he says, “It’s a slower ramp for deployment.” It’s also a long way from the 400-megawatt requirement.
Dominion has found one solution to that problem with its innovative electric school bus program. In a $15 million pilot project started last year, Dominion provided 50 electric school buses to local school systems across Virginia. Pending General Assembly approval, Dominion proposes to put 1,000 electric school buses on the road by 2025 and to completely replace diesel-powered school buses in Virginia by 2030. When not in use, these buses could be used like a fleet of mobile batteries to supply power back to the grid, or to act as mobile power stations during power outages or emergencies. Dominion has estimated that the program would cost each of its Virginia customer households about $12 a year.
Nevertheless, both utilities are moving toward the goal of a carbon-free future, with a certain measure of faith that clean energy and storage technologies will only get better the closer they get to 2045 and 2050.
“In an ideal world, we would be all carbon-free by 2035,” says McClellan, referring to the goal date the Biden administration has set for a carbon-free electricity industry. But 2035 was a no-go in the Virginia General Assembly, and McClellan says she’s comfortable with the 2050 goal and confident that the VCEA provides the framework to meet it.
Since the law’s passage, McClellan says, “We’ve already gone from the back of the pack to the top five or six states [in solar energy generation].”
But the state senator also is a believer in the Russian proverb that became a Ronald Reagan mantra: “Trust but verify.”
“We will be monitoring progress very closely,” McClellan says.
t
















